Forward Exchange Market Table of Contents
- What is a Forward Exchange Market?
- OTC Forward Market
- Forward Exchange Market Keypoints
- Forward Market Process
- Forward Market Price
- Forex Forwards
- Speculation in Forward Market Contracts
- Interest Rates in Forward Exchange Market Contracts
- Forward Exchange Market FAQ
- What is a Forward Exchange Market?
- Forward Exchange Market Keypoints
- Interest Rates in Forward Exchange Market Contracts
Forward Exchange Market In Detail
Forward Exchange Market
The forward exchange market refers to Forex trading in the pre-defined future between two parties who agree to mutually avoid price fluctuations.
In simple terms, the forward exchange market refers to an agreement made between two traders to exchange currencies of two different countries at a specific date in the future.
The spot contract is settled on the agreed date. Usually the arrangement is made to protect the buyers from price fluctuations.
The forward exchange market is also sometimes referred to as a forward exchange contract and it is not traded on exchanges.
The agreement cannot be cancelled under any circumstances unless mutually done by both parties.
In the arrangement both the parties have a common interest to hedge a Forex position or pick up a speculative position.
The rate of exchange between the two parties is fixed and the future date is specified to trade two currencies.
A forward exchange market is designed to safeguard traders from adverse Forex price movement at future dates.
Forward exchange market contracts are usually agreed at one month, three months and one year intervals.
The forward market is an arrangement for trading several financial instruments with certain terms and conditions on the Forex, commodities and securities markets.
OTC Forward Market
Over the counter marketplaces are also known as OTC marketplaces. They facilitate the setting up financial instrument prices or future delivery of financial assets.
Forward Exchange Market Keypoints
A forward exchange market contract is a deal between two traders who want to trade two currencies at a future specified date at the current exchange rate.
Such deals bar the trading of currencies under the terms in the forward exchange market agreement.
It is an arrangement for mutual hedging against fluctuations in the exchange rate and protects both parties from adverse movements.
A Forward Exchange Market contract is utilized by speculators wishing to make a profit or traders who are managing risk with hedging.
Forward Market Process
A forward market leads to forward contracts, which, like futures contracts, is used for speculation as well as hedging. However, the two terms are different. Forward contracts fit the requirements of customers but futures contracts are based on standardized features with respect to maturity and contract size.
It is important to take note here that forwards take place between two banks or between a customer and a bank. Futures, on the other hand, are implemented on exchanges.
Forward Market Price
The forward market price is based on the interest rate. The forward price in Forex is derived from the difference of interest rate of two currencies over the period starting from the date of the transaction to the date of settlement of the contract.
Forex Forwards
Swaps are very common with Forex forwards and many traders in the Forex market understand utilize them.
The interbank forward Forex markets are executed as priced swaps.
Fore example:
Currency X is bought against Currency Y for delivery at the spot rate and on the spot date when the transaction is implemented.
On the date of the maturity date, Currency X is sold against Currency Y at the original spot rate after adjusting the forward points by adding or subtracting to match the agreement.
The interbank market trades periods of month or week from the date of the spot. Usually, the maturity date is in three months or six months from the date swap is initiated.
The financial institution, traders and other customers execute the forward as outright transaction or swap with a bank counter-party. Currency X in this format is purchased against Currency Y for delivery on the date of maturity and this can be done on any business day after the date of the spot.
In this case, too the price tag is the rate of spot along with adjustment of forward points either adding or subtracting. However, the money changes hands only on the date of maturity.
Forwards are synonymous with odd amounts and dates.
Speculation in Forward Market Contracts
Forward market contracts are often traded by speculators wishing to make a profit. Forward market contracts allow a trader to action a trade without having to fund the the whole trade at the time of entering the agreement. The broker or bank actioning the trade may only require some collateral or a deposit.
Traders using forward market contracts do not take full posession of any currency. Traders can buy and sell currency on forward exchange markets and only pay the difference when the forward exchange market contract is due.
This allows forward market contracts to be used for speculation, arbitrage and hedging.
Interest Rates in Forward Exchange Market Contracts
Interest rate differential adjustment is done by either by hiking or slashing prices between the currency pair.
If a currency has lower interest it will be traded at a increased rate.
If it is at a higher interest, it is traded at a decreased amount.
Let us understand it with an example.
If the interest rate is lower in Country A compared to that of Country B, the bank usually adds points to the spot rate. This will result with increase in the foreign currency cost in forward exchange market contracts.
It is important to note that neither party can offload the forward exchange market contract to any third party as it may be very difficult due to the custom price levels.
Due to high level of customization in forward exchange market contracts the offerings from banks cannot compare.
Under most circumstances, the banks charges and fees are higher.
Forward Exchange Volume
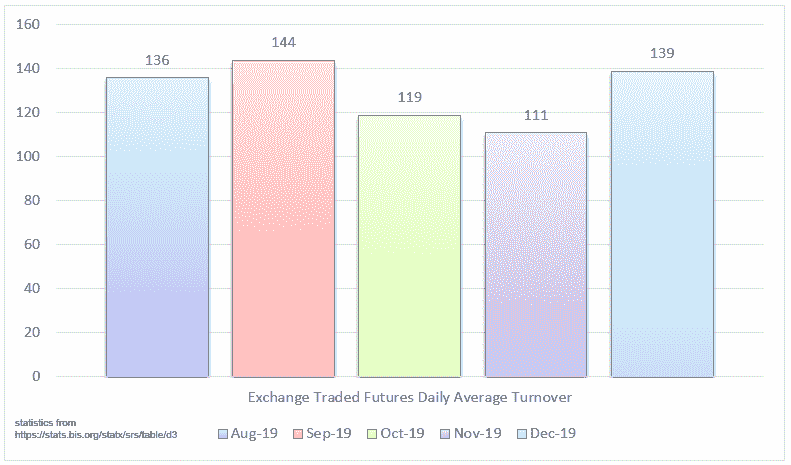
Statistics from the Bank for International Settlements show monthly 2019 Exchange traded currency futures volumes in US dollars (Billions).
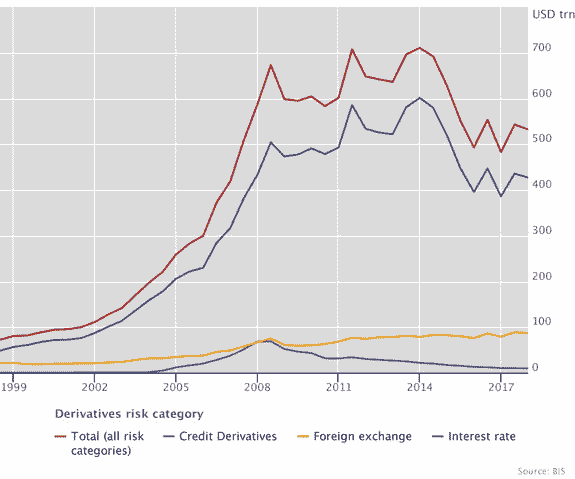
Statistics from the Bank for International Settlements show OTC derivatives statistics by year in trillions of USD. Foreign exchange is the yellow line in the below chart.
You can find more detailed data from the Bank for International Settlements regarding Foreign exchange derivatives here
Forward Market Verdict
The forward market is different from future contracts. The length and size are customizable and interest rate discrepancies define its price.
USD/EUR, USD/GBP and USD/JPY are the mostly traded forward market.
Forward Exchange Market FAQ
What is a Forward Exchange Market?
The forward exchange market refers to Forex trading in the pre-defined future between two parties who agree to mutually avoid price fluctuations.
Forward Exchange Market Keypoints
A forward exchange market contract is an agreement between two traders to trade two currencies at a future specified date at the current exchange rate.
Interest Rates in Forward Exchange Market Contracts
higher interest rates trade at a discount, low interest rates trade at a premium.