Dark Pool Trading Table of Contents
- What is a Dark Pool?
- Dark Pool Advantages
- High Frequency Trading with Dark Pools
- Dark Pool Disadvantages
- Dark Pool Key Highlights
- Dark Pools Verdict
- Volume of dark pool trades
- Types of Dark Pools
- Reasons to own and operate Dark Pools
- Dark Pool Trading FAQ
- What is a Dark Pool?
- Dark Pool Advantages
- Dark Pool Disadvantages
- Types of Dark Pools
Dark Pool Trading In Detail
What is a Dark Pool?
Dark pool is a financial term to describe trading without public visibility until the trade has been completed. Institutional investors can trade huge volumes without intentions being known and it not known in the public eye until it has already gone through. There is a lack of transparency and potential conflicts of interest with dark pools has given them a bad image, but dark pools do serve a purpose.
The dark pool too was first designed in the 1980s for this purpose with the approval of Securities and Exchange Commission for dark pool brokers to place orders for large blocks of assets without the markets being able to impact the trade.
In 2007 SEC made an amendment to the rules to reduce transaction costs and increase competition. Registration Fees were reduced by 71% and transaction fees by up too half. [Source]
This resulted with an increase in the dark pool due to lower fees compared to the exchanges.
A dark pool is associated with lower fees because it is a privately organized platform and is not housed in a bank but within a large firm. An alternative trading system (ATS) allows dark pool investors to trade anonymously in high volume.
Dark Pool Advantages
One of the primary advantages of a dark pool is that institutional investors can place orders of large blocks of shares without it being known in two the public.
This step in fact defends price devaluation. The data of trade execution is revealed after the order is placed and amid such circumstances, it will impact the market less.
High Frequency Trading with Dark Pools
High-frequency trading is dominating volume these days and investors should be thankful for supercomputers equipped with such algorithms that place the orders in just milliseconds.
With the help of HFT technology, institutional investors can trade multi million share bulk orders ahead of rival investors to capitalize on increase or decrease in share prices.
In brief, the high frequency trading gives institutional investors a huge legal advantage over the rest of the market.
Institutional investors are able to trade using HFT several times a day.
Dark Pool Disadvantages
A dark pool is legal but it is widely criticized. Dark pools are criticized for not maintaining complete transparency of trades. HFT is blamed for taking unfair advantage over non dark pool investors.
The SEC has recently taken these complaints seriously and it has created a market monitoring system.
Supporters of dark pools, claim dark pools contribute to vital financial market liquidity and allow global financial markets to function effectively.
Dark Pool Key Highlights
- A dark pool is a financial exchange or forum that is organized privately.
- It provides additional liquidity.
- It maintains the anonymity of the investors until the orders are placed.
- It charges fewer fees compared to other financial platforms.
- The benefits from fewer fees benefit the retail investors.
- Dark Pools lacks transparency.
Dark Pools Verdict
A dark pool is mainly for institutional investors and is not for everyone. It requires a high volume of trade. It is similar to the alternative trading system (ATS) and information of a trade is revealed or reported only after the order is placed.
Volume of dark pool trades in 2020
In the world of securities trading dark pools play an important role. More than fifty dark pool private exchanges were listed at the SEC ending February 2020. Dark pools offer several trading benefits like lower transaction costs and zero exchange fees.
Conceptualized in the 1960s, a dark pool is perfect for institutional investors who seek to buy and sell large orders without disclosing their actions to the public in fear of market distortion.
Dark pool investors can trade in large volumes without rationalizing how their trades will impact the market. Initially, a small fraction of trades represented dark pools in the market.
in the mid 2000’s dark pools counted for around 2 – 5% of all trades in the US markets, but after 2015 there was a boom due to policy changes from regulators, raising to 15 – 18%. [Source Box 2 – Dark pools in the United States]
The SEC passed the National Market System resolution adding new rules to stop trading at prices that are not as good as protected quotations from other trading houses. These rules were set with the intention of restricting price manipulation on the markets. [Source]
Over a period of a decade dark pools were created in large numbers and high frequency trading was embraced by institutional investors.
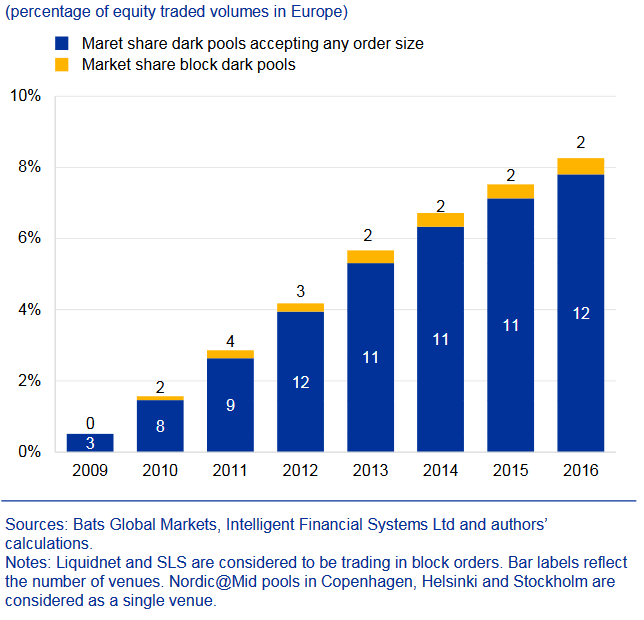
Dark Pool Market share of equities trading in Europe October 2009 to July 2016 In recent years the European market witnessed a jump in the demand for dark pools.
[Source]
After the implementation of the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID), concerned market participants became worried about the transparency of dark pools and boosted trading in the dark with the help of a special pricing mechanism.
However in September of 2019 the European Union introduced rules to curb such trading following 9 percent of dark pool exchange market volumes in the EU regions.
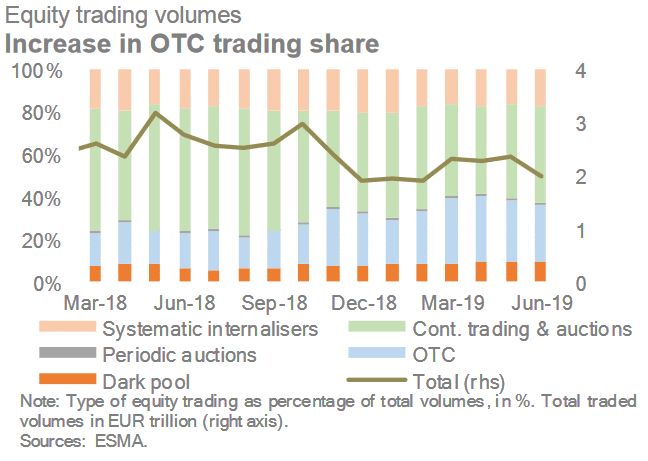
The below snippet is taken directly from the European Securities and Markets Authority 2019 reports of trends, risks and vulnerabilities.
Equity trading volumes in the EU increased in 1H19 but remained below their 2018 levels. More than a year after the entry into force of MiFID II/MiFIR, and in particular the double volume cap (DVC) mechanism, the share of dark pool trading remained low relative to other types of trading, at up too 9% of total trading in 2019.
[Source ESMA Report Infrastructures and Services].
The European Central Bank acts as the main EU bank. It administers monetary policy in the EU. The European Central Bank is one of the most important central banks in the world.
According to the July 2017 newsletter of the European Central Bank, the UBS MTF dark pool use rose from zero to 8% between Q3 of 2009 to Q3 of 2015. It was the highest when compared to other private exchanges trading in European stocks like BXE Book, SIGMA X MTF and ITG Posit. [Source]
Similarly, globally, the CFA Institute plays an important role in curbing dark pools.
The CFA website cites that 32 dark pools actively traded in Q3 of 2009 and it accounted for about 7.9% of the total share volume. [Source]
Formerly known as the Association for Investment Management and Research, the Chartered Financial Analyst creates a code of ethics and establishes top level standards for investment professionals. It is globally-recognized and well respected.
Types of Dark Pools
Basically there are three types of dark pools and those are as below:
Independently Owned
Independent firms or companies own and operate such dark pools.
Broker Dealer Owned
Broker dealers can also own and operate a dark pool. They include financial services firms and banks.
Exchange Owned
Some of the stock exchanges such as BATS Trading and NYSE Euronext own and operate dark pools too.
Reasons to own and operate Dark Pools
There are several reasons to own and operate dark pools. Below are just four of the primary reasons discussed:
- Traders on such dark pools get better price discovery.
- In the US the better price is achieved by following the National Best Bid and Offer (NBBO) regulation.
- Huge volume trades can be kept away from the public exchanges like NYSE.
- The measure is taken to avoid market volatility.
- The possibilities to get buyers for bulk orders increases.
- Dark pools are active even after the closing hours of the public exchanges. So, there is no fixed time for traders to trade.
Dark Pools FAQ
What is a Dark Pool?
Dark pool is a financial term to describe trading without public visibility until the trade has been completed. Institutional investors can trade huge volumes without intentions being known and it not known in the public eye until it has already gone through. There is a lack of transparency and potential conflicts of interest with dark pools has given them a bad image, but dark pools do serve a purpose.
Dark Pool Advantages
One of the primary advantages of a dark pool is that institutional investors can place orders of large blocks of shares without it being known in two the public.
This step in fact defends price devaluation. The data of trade execution is revealed after the order is placed and amid such circumstances, it will impact the market less.
Dark Pool Disadvantages
p>A dark pool is legal but it is widely criticized. Dark pools are criticized for not maintaining complete transparency of trades. HFT is blamed for taking unfair advantage over non dark pool investors.Supporters of dark pools, claim dark pools contribute to vital financial market liquidity and allow global financial markets to function effectively.
Types of Dark Pools
Independently Owned - Independent firms or companies own and operate such dark pools.
Broker Dealer Owned - Broker dealers can also own and operate a dark pool. They include financial services firms and banks.
Exchange Owned - Some of the stock exchanges such as BATS Trading and NYSE Euronext own and operate dark pools too.